Purinergic Library
ChemDiv’s library of small molecule compounds targeting purinergic receptors contains 3,500 compounds.
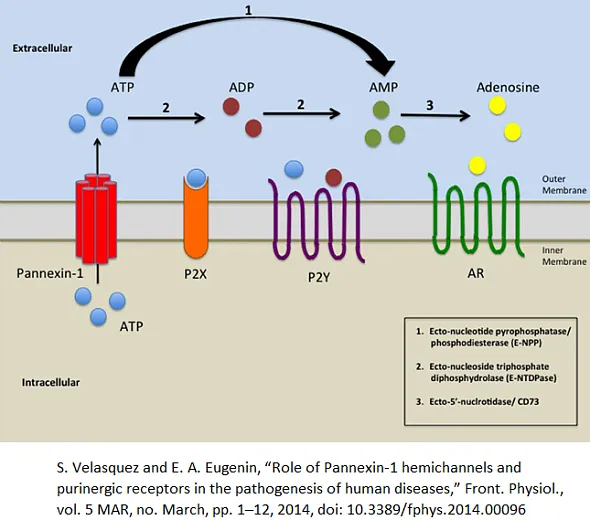
Purinergic receptors play a crucial role in various physiological and pathological conditions of cells. Adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP) acts as a cotransmitter alongside classical transmitters in both the peripheral and central nervous systems. Furthermore, purines serve as potent extracellular messengers to non-neuronal cells, including secretory, exocrine, endocrine, endothelial, immune, musculoskeletal, and inflammatory cells. Alterations in purinergic signaling may arise from abnormal receptor expression or changes in extracellular nucleotide levels. Synthetic modulators for receptors and enzymes involved in purinergic signaling are currently under development [1].
In the gastrointestinal tract, purine nucleosides and nucleotides modulate motor, secretory, and sensory functions, and their dysfunctions. Synthetic modulators of purinergic receptors/enzymes are employed to restore these normal functions. Presently, the development of potent and selective modulators for purinergic signaling offers new therapeutic possibilities for gastrointestinal diseases [2].
Additionally, the therapeutic use of P1 receptor agonists in treating supraventricular tachycardia has been recognized. A2A receptor antagonists show promise in treating Parkinson’s disease. Clopidogrel, a P2Y12 antagonist, is widely used in thrombosis and stroke treatment, as it blocks P2Y12 receptor-mediated platelet aggregation. Research is ongoing for the application of purinergic agents in treating various conditions including osteoporosis, myocardial infarction, epilepsy, atherosclerosis, depression, autism, diabetes, and cancer [1].
References
[1] G. Burnstock, “Purinergic signalling: Therapeutic developments,” Frontiers in Pharmacology, vol. 8. Frontiers Media S.A., Sep. 01, 2017, doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00661.
[2] D. Dal Ben et al., “Approaches for designing and discovering purinergic drugs for gastrointestinal diseases,” Expert Opin. Drug Discov., vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 687–703, 2020, doi: 10.1080/17460441.2020.1743673.